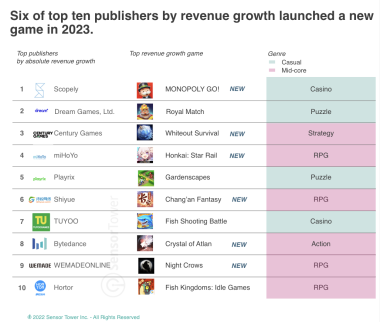
Monetization is an essential aspect of indie game development, and it’s crucial to choose the right strategy to earn revenue from your game. With numerous monetization options available, it can be challenging to choose the most effective strategy for your indie game. In this article, we’ll discuss the top 10 monetization strategies for indie games and how they work.
Fremium Model
The freemium model is one of the most popular monetization strategies for indie games. In this model, the game is free to play, but players can purchase in-game items or access additional features for a fee. This approach allows players to try out the game and decide whether they want to invest in it further. Freemium games often include ads as a way to generate revenue without impacting gameplay.
Pros:
- Widens the Player Base: Since the game is free to play, it attracts a wider audience than games that require upfront payment. This increases the number of players who can try the game and potentially become paying customers.
- Low Barrier to Entry: Freemium games have a low barrier to entry, which means players can start playing the game without investing money upfront. This encourages players to try the game and decide whether they want to invest in it further.
- Can Generate High Revenue: Freemium games can generate high revenue if they have a dedicated player base. Players who enjoy the game are more likely to spend money on in-game items or features, resulting in a steady stream of revenue.
- Provides a Path to Monetization: The freemium model provides a path to monetization for indie developers who may not have the resources to develop a fully paid game. This approach allows developers to create a game and test it in the market without investing heavily upfront.
Cons:
- Balancing Revenue and User Experience: Balancing revenue and user experience is crucial in freemium games. Developers must ensure that the game is enjoyable without in-app purchases and that purchases do not negatively impact gameplay. If the balance is not right, players may feel that the game is pay-to-win, which can be frustrating and turn them away.
- Limited Revenue Streams: Freemium games rely heavily on in-app purchases, which can be a limited revenue stream. Players may not want to spend money on in-game items or features, resulting in lower revenue than other monetization strategies.
- Requires Constant Updates: Freemium games require constant updates to keep players engaged and provide new content for them to spend money on. This can be a challenge for indie developers who may not have the resources to maintain a game long-term.
- Difficulty in Standing Out: With so many freemium games available, it can be challenging to stand out in the market. Developers must create a game that is unique and offers something different from other free-to-play titles.
The freemium model has its pros and cons in indie game development. It can widen the player base, provide a low barrier to entry, and generate high revenue. However, it also requires balancing revenue and user experience, relies on a limited revenue stream, requires constant updates, and can be challenging to stand out in the market. You must carefully consider these factors when choosing a monetization strategy for their indie game.
In-app Advertising
In-app advertising is another popular monetization strategy for indie games. This model involves placing ads within the game to generate revenue. The ads can be banners, interstitials, or videos that play before or after gameplay. In-app advertising can be effective if implemented correctly, but it’s crucial to balance revenue generation with user experience.

Pros:
- No Upfront Cost: Implementing in-app advertising does not require upfront payment, making it an attractive option for indie developers with limited resources. The developer earns revenue from ads without incurring any additional costs.
- Wide Reach: In-app advertising allows developers to reach a wide audience, as players spend significant time in the game. This provides an opportunity for advertisers to promote their products or services to a large number of potential customers.
- Incremental Revenue Stream: In-app advertising provides an incremental revenue stream for indie developers. It allows developers to earn revenue without depending on in-app purchases or paid downloads, which may not be feasible for all players.
- Low Impact on User Experience: In-app advertising can be implemented in a way that has a low impact on the user experience. Ads can be placed in non-intrusive areas and displayed at appropriate times to ensure they don’t negatively impact gameplay.
Cons:
- Can Distract from Gameplay: In-app advertising can be distracting for players and take away from the gameplay experience. If ads are placed in intrusive areas or displayed at inappropriate times, they can negatively impact the game’s user experience.
- May Annoy Players: Ads can annoy players, especially if they are repetitive or displayed frequently. This can result in players leaving the game, resulting in lower engagement and revenue.
- Revenue is Not Guaranteed: In-app advertising revenue is not guaranteed, as it depends on the number of players who view and click on ads. The revenue generated may not be enough to sustain the game’s development and operations.
- Difficulty in Finding Advertisers: Finding advertisers willing to promote their products or services within a game can be challenging, especially for indie developers. Advertisers may prefer to advertise on larger platforms with a larger audience.
It provides a revenue stream without upfront cost, wide reach, incremental revenue, and low impact on user experience. However, it can also distract from gameplay, annoy players, revenue is not guaranteed, and difficulty in finding advertisers. Developers must weigh these factors when considering in-app advertising as a monetization strategy for their indie game. You must also ensure that the ads are placed appropriately, are not intrusive, and do not negatively impact the user experience.
Paid Downloads
Paid downloads are a simple but effective monetization strategy for indie games. Players pay a one-time fee to download the game, and there are no additional charges. This approach is ideal for games with high replay value or those with a unique selling point that sets them apart from free-to-play titles.
Pros:
- High Revenue Potential: Paid downloads have high revenue potential since players pay upfront for the game. This can provide a stable source of income for indie developers and enable them to invest in future projects.
- Low Dependency on In-Game Purchases: Paid downloads provide a low dependency on in-game purchases, which may not be feasible for all players. This makes the game accessible to a broader audience, resulting in more downloads and revenue.
- Minimal Maintenance: Once the game is released, there is minimal maintenance required, as there are no in-game purchases or ads to manage. This allows indie developers to focus on developing new games or updates for existing titles.
- Provides a Sense of Value: Players who pay for the game may feel that they are getting their money’s worth, resulting in a greater sense of value and satisfaction. This can lead to positive reviews, word-of-mouth promotion, and increased sales.
Cons:
- Limited Reach: Paid downloads may have limited reach compared to free-to-play games. Players may not want to invest money in a game they have not tried, resulting in lower downloads and revenue.
- High Risk: Paid downloads are a high-risk monetization strategy since players pay upfront. If the game does not meet the player’s expectations, they may leave negative reviews, which can hurt future sales.
- No Additional Revenue Stream: Paid downloads provide a one-time revenue stream and no additional revenue from in-game purchases or ads. This can limit the game’s long-term revenue potential.
- No Incentive for Continued Engagement: Players who pay for the game may not have any incentive to continue playing after completing it, resulting in lower engagement and potential for additional revenue.
Paid downloads have their pros and cons in indie game development. They offer high revenue potential, low dependency on in-game purchases, minimal maintenance, and provide a sense of value to players. On the other hand, they also have limited reach, are high-risk, provide no additional revenue stream, and no incentive for continued engagement.
Pay-To-Win
Pay-to-win monetization is a controversial strategy that involves offering in-game advantages to players who pay real money. This model can be effective, but it can also be frustrating for players who don’t want to spend money on the game. Pay-to-win is best implemented as a minor part of the game rather than the primary focus.
Pros:
- High Revenue Potential: Pay-to-win has high revenue potential since players pay for in-game advantages. This can provide a stable source of income for indie developers and enable them to invest in future projects.
- Encourages Investment: Pay-to-win encourages players to invest in the game by providing them with advantages they may not otherwise have. This can result in increased engagement and revenue for the developer.
- Provides a Competitive Edge: Pay-to-win provides a competitive edge for players who are willing to spend money on in-game advantages. This can increase the level of competition in the game and result in a more engaging experience for all players.
- Encourages Development: Pay-to-win can encourage developers to continue to develop the game and provide new content and advantages for players to invest in.
Cons:
- Negative User Experience: Pay-to-win can provide a negative user experience for players who do not want to spend money on in-game advantages. This can result in players leaving the game, lower engagement, and potential damage to the game’s reputation.
- Unfair Advantage: Pay-to-win can provide an unfair advantage for players who are willing to spend money. This can result in players who do not pay feeling that they cannot compete and discouraging them from playing the game.
- Poor Reputation: Pay-to-win can result in a poor reputation for the game and the developer. Players may view the game as pay-to-win, which can deter potential players and result in negative reviews.
- Limited Long-Term Potential: Pay-to-win has limited long-term potential since it relies heavily on in-game purchases. Players may become bored with the game if there are no new advantages or content to invest in.
Subscription Model
The subscription model is a popular monetization strategy for games with regular content updates. Players pay a recurring fee to access new content or features, and the revenue generated can be used to support ongoing development. This approach works best for games with a dedicated player base and frequent updates.

Pros:
- Stable Revenue Stream: Subscriptions provide a stable revenue stream for indie developers, as players pay regularly to access new content or features. This can provide a reliable source of income and enable developers to invest in future projects.
- Long-Term Potential: Subscriptions have long-term potential since players continue to pay for access to new content or features. This can result in increased engagement, revenue, and potential for continued development.
- Encourages Development: Subscriptions can encourage developers to continue to develop the game and provide new content and features for players to access.
- Strong Community: Subscriptions can create a strong community around the game, as players who pay regularly have a vested interest in the game’s development and success.
Cons:
- Limited Audience: Subscriptions may have a limited audience compared to free-to-play or paid download games. Players may not want to pay regularly for access to new content or features, resulting in lower engagement and revenue.
- Development Time: Subscriptions require regular development of new content or features to justify the recurring fee. This can be time-consuming and may require more resources than other monetization strategies.
- Difficulty in Balancing Content: Subscriptions require a delicate balance between providing enough new content to justify the recurring fee and not overwhelming players with too much content.
- Difficulty in Building Community: Building a strong community around the game requires consistent engagement and communication with players. This can be challenging for indie developers who may not have the resources to provide ongoing community support.
Sponsorship
Sponsorship is a monetization strategy that involves partnering with a brand or company to promote their products within the game. The sponsor pays the developer a fee, and in exchange, their products or brand are promoted to players within the game. This approach can be effective if the sponsor’s products are relevant to the game and its audience.
Pros:
- High Revenue Potential: Sponsorship has high revenue potential since developers can charge a premium for promoting a company or brand within the game. This can provide a stable source of income for indie developers and enable them to invest in future projects.
- Increased Visibility: Sponsorship provides increased visibility for the game, as it is promoted by the sponsoring company or brand. This can result in increased downloads, engagement, and revenue.
- New Content Opportunities: Sponsorship can provide opportunities for new content within the game, such as branded in-game items or experiences. This can increase the level of engagement and provide a unique experience for players.
- Strong Community: Sponsorship can create a strong community around the game and the sponsoring company or brand. Players may feel more invested in the game and more likely to promote it to others.
Cons:
- Limited Control: Sponsorship may require giving up some control over the game’s content or messaging to the sponsoring company or brand. This can result in a lack of creative freedom for the developer.
- Negative Perception: Sponsorship can result in a negative perception of the game or the developer, especially if the sponsoring company or brand is controversial or unpopular.
- Risk of Oversaturation: Sponsorship can result in oversaturation of the game with the sponsoring company or brand’s messaging. This can negatively impact the user experience and turn players away.
- Limited Long-Term Potential: Sponsorship has limited long-term potential since it relies heavily on one-time deals with sponsoring companies or brands. This can limit the game’s potential for continued revenue and development.
Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding is a popular way for indie developers to raise funds to develop their games. Platforms like Kickstarter and Indiegogo allow developers to pitch their game to potential backers, who can then pledge money to support the project. Crowdfunding can be an effective way to fund development while building a community around the game.

Pros:
- High Revenue Potential: Crowdfunding has high revenue potential since backers can contribute significant amounts of money to support the game’s development. This can provide a stable source of income for indie developers and enable them to invest in future projects.
- Provides Market Validation: Crowdfunding provides market validation for the game, as it shows that there is a community of backers willing to support its development. This can increase the game’s credibility and make it more attractive to potential players.
- Community Building: Crowdfunding can create a strong community around the game, as backers have a vested interest in the game’s success. This can result in increased engagement, word-of-mouth promotion, and potential for continued development.
- Creative Freedom: Crowdfunding provides creative freedom for indie developers since they are not beholden to the demands of publishers or investors. This can result in a more unique and innovative game.
Cons:
- Risk of Failure: Crowdfunding has a risk of failure since there is no guarantee that the game will be successful or that backers will receive a return on their investment. This can result in negative publicity and potential damage to the developer’s reputation.
- Time-Consuming: Crowdfunding can be time-consuming, as developers must create a campaign, market it effectively, and engage with backers. This can take away from development time and require more resources than other monetization strategies.
- Limited Reach: Crowdfunding may have a limited reach compared to free-to-play or paid download games. Backers may not want to invest money in a game they have not tried, resulting in lower engagement and revenue.
- Requires Transparency: Crowdfunding requires transparency from developers, as backers expect regular updates on the game’s development progress. This can be challenging for developers who may not want to reveal too much about the game before its release.
Merchandise
Merchandise sales are an effective way to monetize an indie game’s popularity. T-shirts, plushies, posters, and other merchandise can be sold to fans of the game, generating revenue and building brand recognition. This approach is best used for games with a strong following.
Pros:
- High Revenue Potential: Merchandise sales have high revenue potential, as fans are often willing to pay a premium for physical products related to their favorite games. This can provide a stable source of income for indie developers and enable them to invest in future projects.
- Increased Brand Recognition: Merchandise sales can increase brand recognition for the game, as fans wear or display the products in public. This can result in increased downloads, engagement, and revenue.
- Strong Community: Merchandise sales can create a strong community around the game, as fans have a tangible way to express their love for the game. This can result in increased engagement and loyalty.
- Minimal Maintenance: Once the merchandise is designed and produced, there is minimal maintenance required, as there are no in-game purchases or ads to manage. This allows indie developers to focus on developing new games or updates for existing titles.
Cons:
- Requires Investment: Merchandise sales require significant investment from developers to design and produce products. This can take away from development time and require more resources than other monetization strategies.
- Limited Reach: Merchandise sales may have a limited reach compared to free-to-play or paid download games. Fans may not want to invest in physical products related to a game they have not tried, resulting in lower engagement and revenue.
- Difficulty in Marketing: Merchandise sales require effective marketing to reach a broad audience and increase sales. This can be challenging for indie developers who may not have the resources to effectively market their products.
- Limited Long-Term Potential: Merchandise sales have limited long-term potential since they rely heavily on the popularity of the game. If the game loses popularity, revenue from merchandise sales may decline.
eSport
Esports and tournaments are a growing area of the gaming industry, and indie developers can take advantage of this trend by hosting their own competitions. Players pay an entry fee to compete, and the prize money is generated from those fees. Esports and tournaments can generate significant revenue for the developer, but they require a dedicated player base and infrastructure to support them.

Pros:
- High Revenue Potential: Esports and tournaments have high revenue potential, as players and spectators pay for tickets or access to events. This can provide a stable source of income for indie developers and enable them to invest in future projects.
- Increased Visibility: Esports and tournaments provide increased visibility for the game, as they are often streamed or broadcast to a large audience. This can result in increased downloads, engagement, and revenue.
- Competitive Edge: Esports and tournaments provide a competitive edge for players who are looking for a challenge and recognition. This can increase engagement and create a loyal fan base for the game.
- Strong Community: Esports and tournaments can create a strong community around the game and the esports scene. Players may feel more invested in the game and more likely to promote it to others.
Cons:
- High Barrier to Entry: Esports and tournaments have a high barrier to entry since players must be skilled enough to compete. This can result in a limited audience and potential for lower engagement and revenue.
- Requires Investment: Esports and tournaments require significant investment from developers to organize and promote. This can take away from development time and require more resources than other monetization strategies.
- Difficulty in Building Community: Building a strong community around esports and tournaments requires consistent engagement and communication with players and fans. This can be challenging for indie developers who may not have the resources to provide ongoing community support.
- Limited Long-Term Potential: Esports and tournaments have limited long-term potential since they rely heavily on the popularity of the game and the esports scene. If the game or the scene loses popularity, revenue from esports and tournaments may decline.
DLC’s
Downloadable content (DLCs) are additional content or features that can be purchased after the initial release of the game. DLCs are an effective way to generate additional revenue from players who have already purchased the game. This approach works best for games with established community and stable gameplay.
Pros:
- High Revenue Potential: DLC has high revenue potential since players pay for additional content after the initial release of the game. This can provide a stable source of income for indie developers and enable them to invest in future projects.
- Increased Engagement: DLC can increase engagement for players who are invested in the game and want new content to explore. This can result in increased downloads, engagement, and revenue.
- Provides a Competitive Edge: DLC can provide a competitive edge for players who purchase it, such as new characters or items. This can increase the level of competition in the game and result in a more engaging experience for all players.
- Provides Long-Term Potential: DLC has long-term potential since players can continue to purchase new content over time. This can result in increased revenue and potential for continued development.
Cons:
- Negative User Experience: DLC can provide a negative user experience for players who feel that they are being charged for content that should have been included in the initial release of the game. This can result in players leaving the game, lower engagement, and potential damage to the game’s reputation.
- Unfair Advantage: DLC can provide an unfair advantage for players who are willing to pay for additional content. This can result in players who do not pay feeling that they cannot compete and discouraging them from playing the game.
- Poor Reputation: DLC can result in a poor reputation for the game and the developer if players perceive that they are being taken advantage of or that the DLC is low-quality or unnecessary.
- Limited Long-Term Potential: DLC has limited long-term potential since it relies heavily on the release of new content. If the game stops receiving new DLC, players may become bored and disengage from the game.
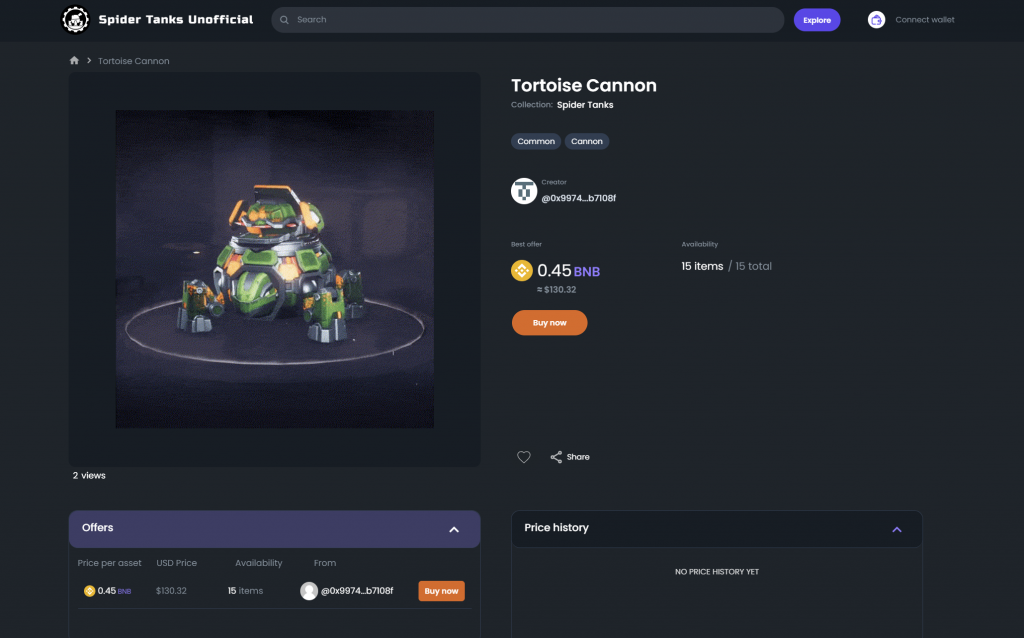
Web3
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have gained immense popularity in the world of art, music, and sports, but they have also found their way into the world of video games. Indie game developers have started implementing NFTs in their games as a way to monetize their creations. While this strategy has its advantages, it also comes with its fair share of disadvantages. Let’s take a closer look at the pros and cons of monetization through NFTs in indie games.
Pros:
- Increased Revenue: NFTs offer game developers a new way to generate revenue. Instead of relying solely on traditional methods such as game sales, in-game purchases, or subscription-based models, developers can sell unique in-game items as NFTs. As NFTs are rare and one-of-a-kind, they can be sold for a higher price, which can boost a developer’s revenue.
- Increased Player Engagement: NFTs can increase player engagement by providing them with unique in-game items that are scarce and difficult to obtain. Players can purchase or trade NFTs with other players, which can create a sense of ownership and exclusivity. This can encourage players to spend more time in the game, which can lead to increased revenue for the developer.
- Protection of Intellectual Property: NFTs can be used to protect the intellectual property of game developers. By creating unique in-game items as NFTs, developers can ensure that their creations cannot be duplicated or stolen. As NFTs are based on blockchain technology, they provide a secure and transparent way of verifying ownership.
Cons:
- Environmental Concerns: The creation of NFTs requires a significant amount of energy, which has raised concerns about their environmental impact. As NFTs are based on blockchain technology, they require a significant amount of computing power to create and maintain. This energy consumption can contribute to carbon emissions, which can harm the environment.
- Exclusivity: NFTs are designed to be exclusive, which means that only a limited number of players can own them. This can create a sense of inequality among players, as those who cannot afford to purchase NFTs may feel left out. This can lead to a decline in player engagement, which can harm the developer’s revenue.
- Legal Concerns: The use of NFTs in games can raise legal concerns, particularly around ownership and copyright. As NFTs are based on blockchain technology, it can be difficult to determine who owns them and who has the right to sell them. This can lead to legal disputes, which can harm the developer’s reputation and revenue.