For the general public, the terms mining and cryptocurrencies always come hand in hand. Those familiar with the crypto market have probably heard of two ways of validating transactions: Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). As of 2021, PoW is still dominating the market, but PoC is gaining prominence. This text is going to discuss those two consensus mechanisms in detail and look at the reasons behind the shift.
The Proof of Work Consensus
Proof of Work is the concept that gave birth to Bitcoin and then to cryptocurrencies in general. It is precisely what is commonly referred to as “mining” bitcoins. Explaining in simple words: it’s performing computation to solve random equations.
Of course, as with many things in the world, the Proof of Work is a more complex issue. In the following paragraphs, we’re going to take a closer look at it. We will start from its history (closely interwoven with Bitcoin). Then we will explain what it is. Finally, we will discuss issues that arose around the PoW during the years.
The Beginning – Bitcoin
Bitcoin was born in 2010. Like anything that is decentralized, it needed to adopt some kind of consensus mechanism to control the credibility of transactions. The inventor or inventors of Bitcoin going under the name Satoshi Nakamoto decided to found his coin and the entire blockchain on the consensus named Proof of Work. At that time, it may have seemed like a perfect solution.
Bitcoin and blockchain were at first embraced only by a handful of enthusiasts, leaving Nakomoto free of worries about the speed and performance of the algorithms he suggested. Solving complex cryptographic equations guaranteed the security of transactions and the stability of the entire system.
The Name
Actually, the adoption of proof of work consensus was so unquestionable at the beginning that the entire phenomenon took the name from it. At first, it was just Bitcoin and blockchain, both named by their investors, but with more and more “coins” emerging, the entire market needed the name.
Because it was cryptographic equations that constituted the very essence of coins’, the market was dubbed crypto. Soon cryptocurrencies started to gain popularity. The idea of a decentralized financial system seemed to strike the perfect moment. With the world struggling with the consequences of the 2008 financial crisis, the concept of currency independent from any financial institution was very tempting.
Bitcoin and Altcoins
Although the crypto market in 2021 is huge and encompasses many different financial instruments (check our texts about the NFTs or crypto gaming), it’s still primarily divided into Bitcoin and “the rest.” Other coins are often referred to as Altcoins.
The first Altcoin was Litecoin in 2011. It became the beginning of the trend. Each new crypto wanted to distinguish itself from bitcoin, yet they all depended on the proof of work.
Ethereum
2015 witnessed the birth of the cryptocurrency that is now the second most popular one. Ethereum is now worth more than 390 billion dollars. But it’s important for another reason. Ethereum enabled “smart contracts,” opening the door for entirely new crypto possibilities. NFT market and crypto gaming are both connected with this shift.
Ethereum was a revolutionary step for the crypto market. However, since it was 2015, it was still based on proof of work. Although Proof of Stake Consensus was first described in 2012, 2015 still smelled like Proof of Work.
Proof of Work – How It Works?
Proof of Work is the foundation of Bitcoin and the crypto market as a whole. But what is it exactly? And how does it work?
The data about Bitcoin transactions are stored in a publicly accessible ledger – that’s, blockchain. As the name suggests, blockchain is a chain of blocks each containing data about 745 Bitcoin transactions. For Bitcoin, a new block is generated every ten minutes. Proof of Work is a way in which new blocks are generated and validated.
To generate a new block the data from previous blocks are put through the hash function (bitcoin uses SHA-256). The first computer that arrives at the correct hash generates the new block and is awarded a certain amount of bitcoins. Since the computation is very demanding, the process requires a significant amount of “work” – hence the name proof of work.
The Issues with PoW
As of 2021, around 65% of cryptocurrencies is based on the Proof of Work consensus. So why change anything? The market seems to be quite well.
Apparently, what was suitable for a small project targeted at a bunch of enthusiasts is much less fitted for a serious endeavor addressed to the general public. Proof of Work is now facing at least three significant charges.
Three main problems with the Proof of Work consensus are:
- energy consumption
- transaction speed
- transaction costs
We will tackle each of these issues in a separate paragraph below.
Energy Consumption
We already said that mining Bitcoins (or other PoW based coins) requires solving non-trivial computational problems, which involves using powerful hardware and a lot of electricity. It wasn’t an issue when crypto was a niche. But the rise in popularity of cryptocurrencies resulted in more interest in mining activities. The power demand went through the roof.
Right now, the power consumption of Bitcoin mining only in China reaches the power demand of Italy. In the era of rising environmental consciousness, such an issue could not go unnoticed, especially in the view of the news like those from Australia, where the coal power plant was reactivated only to power up the Bitcoin mining facility.
The Speed
The original Bitcoin blockchain code was able to process only seven transactions per second. Ethereum developers made a few changes and doubled this number, but fifteen transactions per second is still not a very impressive number for a global currency.
Once again, the Proof of Work consensus seems to lose its attractiveness with scale. The growing market for cryptocurrencies demands a faster solution.
The Cost
This headline can be read from two different perspectives:
- The cost of a single crypto transaction
- The cost of electricity needed to keep blockchain up and running
It should not come as a surprise that both of those costs skyrocketed with the growing popularity of PoW based cryptocurrencies.
At the beginning, the cost of a single Bitcoin transaction amounted to a fraction of a cent. Yet in 2021, the fee reached 60 dollars. It has dropped significantly since then, but the days of cheap transactions are gone. For the record: Ethereum transaction fee is somewhat around five dollars – less than sixty, but far for a cent.
We’ve already discussed the power consumption related to Proof of Work from the environmental perspective, but this is just one side of the problem. The inventors of the Proof of Stake consensus estimated in 2012 that blockchain required 150 thousand dollars daily to pay its electricity bills. What would be the amount today? Certainly not negligible.
Tutaj chciałabym przerobić ten wykres: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bitcoin_electricity_consumption.png
That’s why the discussion about switching to some other kind of consensus is gaining more and more attention among crypto enthusiasts. The most promising proposal by far is called the Proof of Stake.
The Proof of Stake Consensus
The proof of Stake consensus was proposed in 2012 by Scott Nadal and Sunny King as a solution to the disputes arising around the PoW. It is claimed that switching cryptocurrencies to the Proof of Stake could help them become more “green” while at the same time improving their performance.
Obviously, PoC consensus is not a perfect solution itself. It has some drawbacks, which we will discuss in the following paragraphs. In 2021 only altcoins are based on it. However, the discussion around its wider adoption has been on for some time now. Ethereum – the second biggest crypto – has already moved from PoW to PoC soon.
Having said that, in 2021, it’s definitely important to be familiar with the Proof of Stake consensus.
Proof of Stake – How It Works?
The idea behind the PoS is entirely different than the PoW. Though it still relies on solving cryptographic equations, there is no “mining” involved.” Instead, the process is called “forging,” and the creator of a new block only earns transaction fees. No new coins are created in the process.
How does it solve the issue of power demand? There is no race to solve the puzzle first. The creator of the new block is chosen basing on the number of coins they staked in a special wallet. Of course, to provide stability, there is a minimal amount you have to invest to start forging.
The use of PoC eliminates the unnecessary computations done only to take part in a race for mining new coins. Proof of Stake algorithm randomly chooses the forger of a new block, and the chances are proportional to the investment made.
The Issues with PoS
Adoption of the Proof of Stake Consensus addresses the environmental issues with cryptocurrencies in a very elegant way. It is even somehow protected against the 51% attack. But it has problems of its own.
Some argue that the linear dependency between the coins owned and the fees earned. In simple words: PoS makes the rich even richer. On the other hand, though, the investment needed to build a Bitcoin mining farm is not trivial either.
The more serious dispute is about the vulnerability to so-called Nothing at Stake Attack. This issue is still under debate, and several solutions are proposed. One of them being the introduction of the proof of misbehavior locking such users from validating transactions.
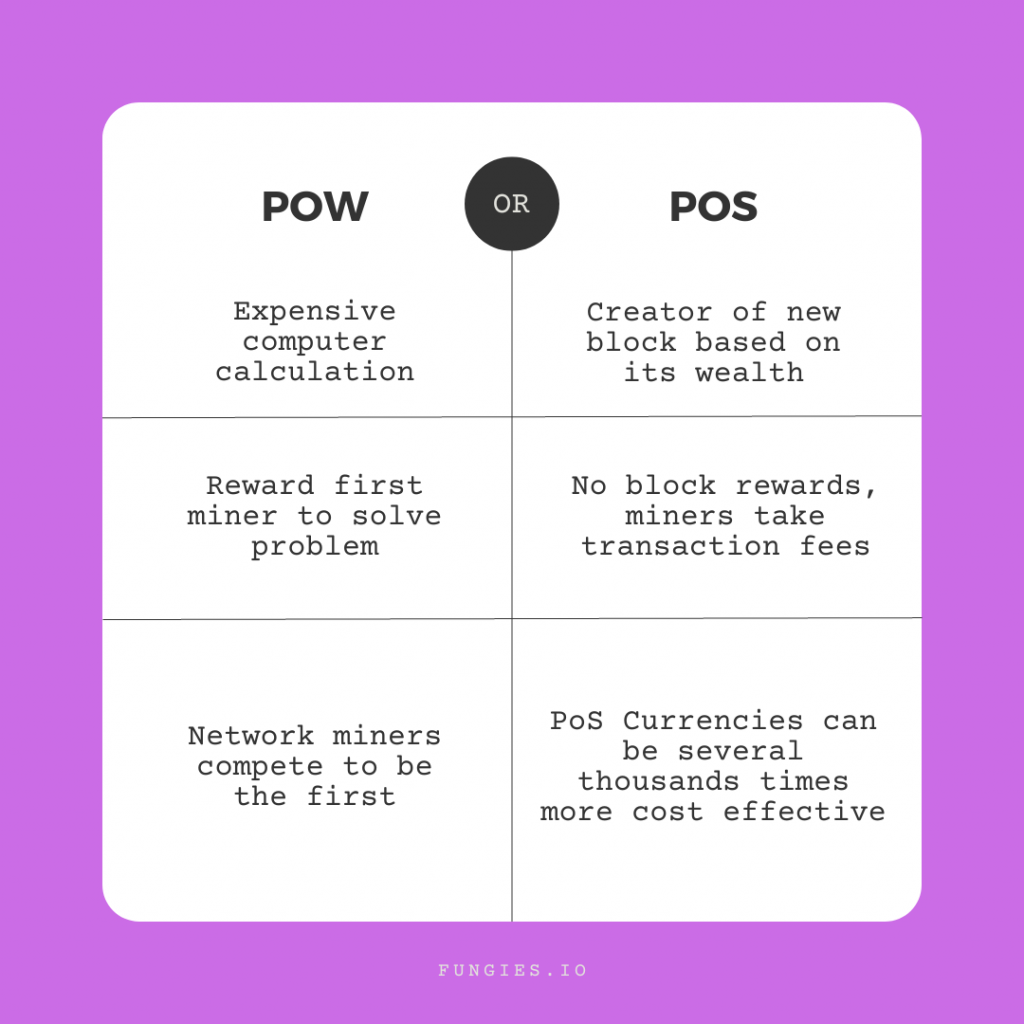
PoW and PoS Compared
Now that we already discussed the Proof of Work and Proof of Stake in detail, it’s time to compare the two.
| Proof of Work | Proof of Stake | |
| Creation of new blocks | New blocks are created by mining | New blocks are created by forging |
| Creators | Miners compete to create a new block | The creator of a new block is chosen randomly based on their stake. |
| Prize | The creator of a block earns new coins | There is no block reward, only the transaction fee |
| Power | Farms are running 24/7 using vast amounts of energy to arrive at the solution first and earn new coins | Only the chosen forger runs the algorithm. |
| Coins | Bitcoin | Altcoins and soon Ethereum |
| Vulnerability | 51% attack | Nothing at Stake Attack |
Summary
Right now, the crypto market is dominated by two leading solutions of confirming transactions – Proof of Work and Proof of Stake. The first was born with the birth of Bitcoin, the second is responding to problems bugging Bitcoin due to its popularity. While the present undeniably belongs to the PoW, with Ethereum considering switching to PoC, it appears that the future lies there.