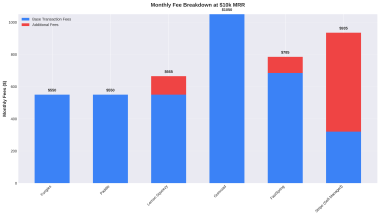
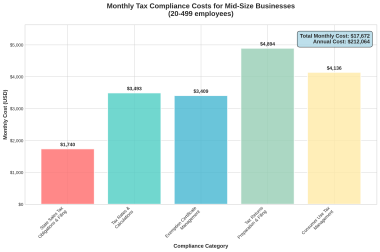
As a SaaS (Software as a Service) business owner, ensuring sales tax compliance is a critical responsibility that can significantly impact your company’s success and growth. Failure to collect and remit sales taxes can lead to severe consequences, including hefty fines, legal issues, and reputational damage. In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore the importance of sales tax compliance, the consequences of non-compliance, and the steps you can take to stay on top of your tax obligations.
Understanding Nexus and Sales Tax Collection
The concept of “nexus” is the foundation of sales tax compliance. It determines whether your SaaS business has a tax obligation in a particular state or country. If your company has a physical presence, such as offices or employees, or an economic presence that exceeds certain revenue or sales thresholds in a region, you may be required to collect sales taxes from customers in that area.In the United States, the 2018 South Dakota v. Wayfair Supreme Court ruling has significantly changed the sales tax landscape. Many states have since implemented economic nexus laws, which means that even if you don’t have a physical presence in a state, you may still need to collect sales tax from customers there if you exceed certain revenue or transaction thresholds.Internationally, the rules are equally complex. Countries like the European Union, Canada, Australia, and India require SaaS providers to collect VAT (Value-Added Tax) or GST (Goods and Services Tax) from customers within their borders.
The Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to collect and remit sales taxes can have severe consequences for your SaaS business. Let’s take a closer look at the potential repercussions:
- Financial penalties: Tax authorities can impose steep fines and interest for non-compliance, which can quickly add up and significantly impact your bottom line.
- Audits: Your business may be subject to costly and time-consuming tax audits, during which authorities will assess how much tax is owed and impose penalties for underpayment. These audits can be a significant drain on your resources and disrupt your day-to-day operations.
- Legal liability: In some cases, tax authorities can hold you personally liable for unpaid taxes, requiring you to cover the tax amount out of your own funds instead of passing it on to customers. This can be a devastating blow to your company’s cash flow and financial stability.
- Reputational damage: Not complying with tax regulations can erode trust with customers and business partners, harming your company’s reputation and making it harder to attract new clients and retain existing ones.
- Severe legal consequences: In extreme cases, willfully avoiding tax collection or payment could result in lawsuits or even criminal charges, which can be devastating for your business and personal life.
Here is a table outlining tax rates (primarily VAT/GST for SaaS businesses), along with common penalties for non-compliance in various countries. Please note that tax rates and penalties may vary depending on specific circumstances, such as the business size and the nature of the violation.
| Country | VAT/GST Rate for SaaS | Penalties for Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Varies by state (e.g., 6-10% for sales tax) | Penalties vary by state, but typically include: fines (up to 25% of the unpaid tax), interest on unpaid taxes, and potential criminal charges for willful evasion. |
| European Union | 15-27% (varies by country) | Late filing penalties up to €10,000 or more; interest on unpaid VAT; severe cases can lead to criminal prosecution with additional fines and potential imprisonment. |
| United Kingdom | 20% VAT | Penalties up to 100% of the unpaid tax, late payment interest, and a £400 fine for late filings. Deliberate non-compliance can result in criminal charges and prison sentences. |
| Canada | 5% GST + provincial taxes (varies, 5-15%) | Late filing penalties of 1% of the overdue amount plus daily interest. Continuous failure may result in higher penalties and criminal charges. |
| Australia | 10% GST | Penalties include fines starting at AUD $222 per penalty unit, up to 75% of the unpaid tax for severe non-compliance. Repeated or intentional violations may result in criminal prosecution. |
| India | 18% GST | Penalties include a fine of 10% of the tax due, up to ₹10,000, and 100% of the tax in cases of deliberate evasion. Late payment incurs interest at 18% per annum. |
| Japan | 10% Consumption Tax | Late filing penalties are 15-20% of the underreported tax amount, plus an additional daily interest charge. For serious fraud, penalties can be up to 35% of the tax due, plus imprisonment. |
| Brazil | 17-25% (varies by state) | Fines up to 150% of the unpaid tax for willful evasion, interest on unpaid amounts, and criminal charges for fraud. Administrative penalties can also be imposed for late filings. |
| New Zealand | 15% GST | Penalties include a 1% late payment penalty, plus interest. Severe non-compliance can result in penalties of up to 150% of the tax due and criminal charges for deliberate evasion. |
| South Africa | 15% VAT | Penalties can be up to 200% of the unpaid tax, depending on the nature of non-compliance. Interest is also charged on late payments, and criminal prosecution is possible for fraud. |
| Singapore | 8% GST | Late filing incurs penalties of SGD $200 per month, up to a maximum of SGD $10,000, with an additional 5% surcharge on unpaid taxes. Severe cases may result in criminal prosecution. |
| Norway | 25% VAT | Late payment penalties include interest plus fines of up to 20% of the unpaid amount. Severe non-compliance can result in criminal charges and imprisonment. |
| Switzerland | 7.7% VAT | Penalties include fines of up to 50% of the tax owed, plus interest. In cases of deliberate fraud, penalties can be as high as 300% of the tax due, and criminal prosecution is possible. |
Important Notes:
- Penalties: These are general penalties, and specific fines or interest rates can vary depending on the nature of non-compliance (e.g., failure to file, underreporting, fraud, etc.).
- Tax Rates: VAT/GST rates listed are primarily for SaaS services and may be subject to specific exemptions or special rules in certain jurisdictions.
This table provides an overview of VAT/GST rates and penalties for tax non-compliance in some of the most significant markets for SaaS businesses. If you’re operating in multiple jurisdictions, it’s essential to consult with a tax professional for specific advice tailored to each region.
Common Taxes SaaS Companies Need to Consider
As a SaaS business, you’ll need to navigate a complex web of sales tax regulations. Here are some of the most common taxes you’ll need to consider:
- Sales tax (U.S.): As mentioned, the U.S. has a patchwork of state-by-state sales tax laws that many SaaS companies must navigate. Each state has its own rules and regulations, and it’s crucial to stay on top of these changes to avoid penalties.
- VAT/GST (International): Depending on where your customers are located, you may need to collect VAT or GST, typically charged as a percentage of the sale price. Failing to collect and remit these taxes can lead to significant penalties and legal issues.
- Income tax: In addition to sales tax, you’ll also need to file income tax in jurisdictions where you have a significant presence. This includes both federal and state income taxes in the U.S., as well as international income taxes if you have operations or employees in other countries.
- Digital Services Taxes (DST): Some countries have introduced a DST on revenues from digital services provided to local customers, which may affect your SaaS business depending on where you operate. These taxes are relatively new and can be complex to navigate, so it’s essential to stay informed and consult with tax professionals.
Steps to Ensure Compliance
To stay compliant with sales tax regulations, SaaS businesses should take the following steps:
- Identify nexus: Determine where you have nexus based on your physical or economic presence and consult tax professionals or software tools to stay compliant with tax laws in those areas. This may involve registering with state or local tax authorities and obtaining the necessary permits and licenses.
- Use tax software: Implement automated tax software like Avalara, TaxJar, or Stripe’s integrated tax tools to calculate, collect, and remit taxes appropriately. These tools can help you stay on top of changing regulations, ensure accurate calculations, and streamline the tax filing process.
- Register for tax IDs: Register with local tax authorities in different states or countries to legally collect taxes. This may involve obtaining a sales tax permit, a resale certificate, or a VAT/GST registration number, depending on your location and the taxes you need to collect.
- Consult tax experts: Seek guidance from tax professionals who specialize in SaaS businesses to ensure you meet all requirements, as tax regulations can be complex and vary widely across regions. These experts can help you navigate the nuances of sales tax compliance, minimize your tax liability, and ensure you stay on the right side of the law.
- Keep accurate records: Maintain detailed records of all sales transactions, including the location of the customer, the amount of the sale, and the taxes collected. This documentation can be crucial in the event of an audit and can help you demonstrate your compliance efforts to tax authorities.
- Stay informed: Stay up-to-date with changes in sales tax regulations by subscribing to industry newsletters, attending webinars, and participating in online forums. This will help you anticipate changes and adjust your compliance strategies accordingly.
- Automate and streamline: Use technology to automate and streamline your sales tax compliance processes. This can include integrating your e-commerce platform with tax software, setting up automatic tax calculations and remittances, and using cloud-based tools to manage your compliance efforts.
By prioritizing sales tax compliance, SaaS businesses can avoid legal trouble, financial loss, and reputational damage while maintaining a solid relationship with customers and authorities. It’s a complex and ever-evolving landscape, but by taking proactive steps and working with tax professionals, you can ensure your business stays on the right side of the law and continues to thrive.
The Importance of Staying Compliant
Sales tax compliance is not just a legal obligation; it’s a strategic imperative for SaaS businesses looking to succeed in today’s competitive landscape. By staying on top of your tax obligations, you can:
- Avoid costly penalties and legal issues: Failing to collect and remit sales taxes can lead to significant fines, audits, and even legal action. By prioritizing compliance, you can protect your business from these risks and focus on growth and innovation.
- Build trust with customers: Customers want to do business with companies they can trust. By demonstrating your commitment to compliance, you can build stronger relationships with your clients and position your business as a reliable and trustworthy partner.
- Streamline your operations: Automating and streamlining your sales tax compliance processes can save you time and money, freeing up resources that you can invest in other areas of your business.
- Gain a competitive edge: In a crowded SaaS market, compliance can be a differentiating factor. By demonstrating your commitment to staying on top of tax regulations, you can set your business apart from the competition and attract more customers.
- Prepare for growth: As your SaaS business grows and expands into new markets, staying compliant will become even more critical. By laying the groundwork for compliance now, you can position your company for long-term success and make it easier to scale in the future.
Conclusion
Sales tax compliance is a critical issue for SaaS businesses of all sizes. By understanding the concept of nexus, navigating the complex web of sales tax regulations, and taking proactive steps to ensure compliance, you can protect your business from costly penalties and legal issues while building trust with customers and positioning your company for long-term success.Remember, sales tax compliance is not a one-time task; it’s an ongoing process that requires vigilance, attention to detail, and a willingness to adapt to changing regulations. By staying informed, working with tax professionals, and using technology to streamline your compliance efforts, you can ensure that your SaaS business stays on the right side of the law and continues to thrive in the years to come.