The gaming industry has faced a tumultuous year, marked by significant challenges and transformative shifts. Numerous game studios have shuttered, resulting in widespread layoffs and altering the dynamics of the job market due to an increase in studio consolidations. Amidst this backdrop, the emergence of generative AI is creating a buzz for its potential to boost productivity, though it also raises concerns about further disruptions in the industry.
However, every challenge brings new possibilities. The surge in adaptations of games into films and TV series is attracting a fresh wave of audiences to the gaming world. Game studios are actively exploring innovative uses of game engines, and the momentum for unionization is building, particularly among the younger segment of game developers, with instances of union formation within companies.
To gain deeper insights into these trends, we conducted a comprehensive survey involving over 3,000 game developers, delving into their perspectives on their work and the broader gaming industry. The findings are revealing: developers are increasingly focusing on incorporating accessibility features in their games, showing signs of growing disillusionment with social media, and displaying mixed views regarding policies on mandatory office returns.
The 2024 State of the Game Industry survey, now in its twelfth year, continues to provide valuable insights into the evolving landscape of the gaming industry. This year, the Game Developers Conference (GDC) partnered with Omdia for an in-depth analysis of the survey data, offering unprecedented detail. Additionally, this year’s report marks a continued collaboration with Game Developer, combining efforts to enhance the context and clarity of the survey findings.
A key finding from the report highlights the issue of job losses in the gaming sector, a topic of significant concern for many professionals. Insightful comments from developers, such as the observation that “Studios grew too quickly during the pandemic,” shed light on the situation. This perspective aligns with industry data, which indicates a substantial increase in revenue during 2020 and 2021 — approximately $50 billion more than projected, attributed to the Covid-19 pandemic. However, the years 2022 and 2023 witnessed a return to pre-2020 spending patterns, suggesting that the recent cutbacks in workforce are a delayed response to a less favorable market environment.
Looking forward, industry forecasts predict a return to steady growth through to 2027. This projection suggests a more stable environment for employment in the gaming sector in the coming years.
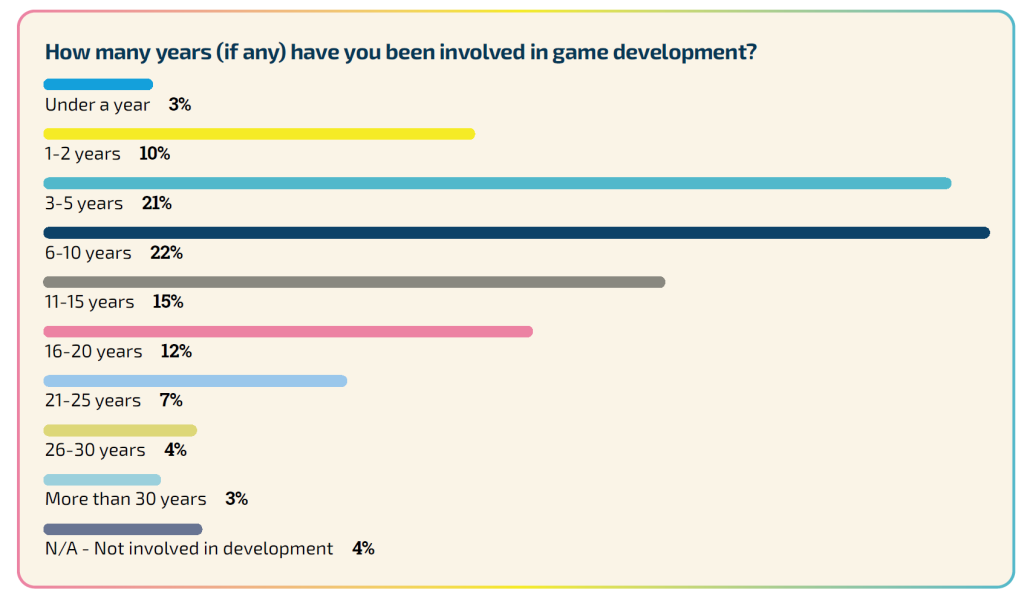
Most game developers possess under a decade of experience, typically employed at smaller studios.
Consistent with past trends, 56% of survey participants have engaged in game development for 10 years or less.
This year’s analysis delved into the demographic makeup of the longest-serving members in the gaming industry—the seasoned decision-makers who have been part of this domain for decades. The survey revealed that a substantial majority of these veterans are men, with 87% of game developers having more than 21 years of experience in the industry identifying as male. Among these, white men form the largest demographic, representing 92%.
When the survey data was segmented by race and gender, it showed that Asian men comprised 15%, while Hispanic, Latino, or Spanish-origin men made up 8%, and Black men accounted for 6%. Both white and Asian women were represented equally, each constituting 5% of those with over 20 years of experience in game development. Notably, the survey found no representation of Black women or Hispanic, Latino, or Spanish-origin women among those with the same level of industry experience.
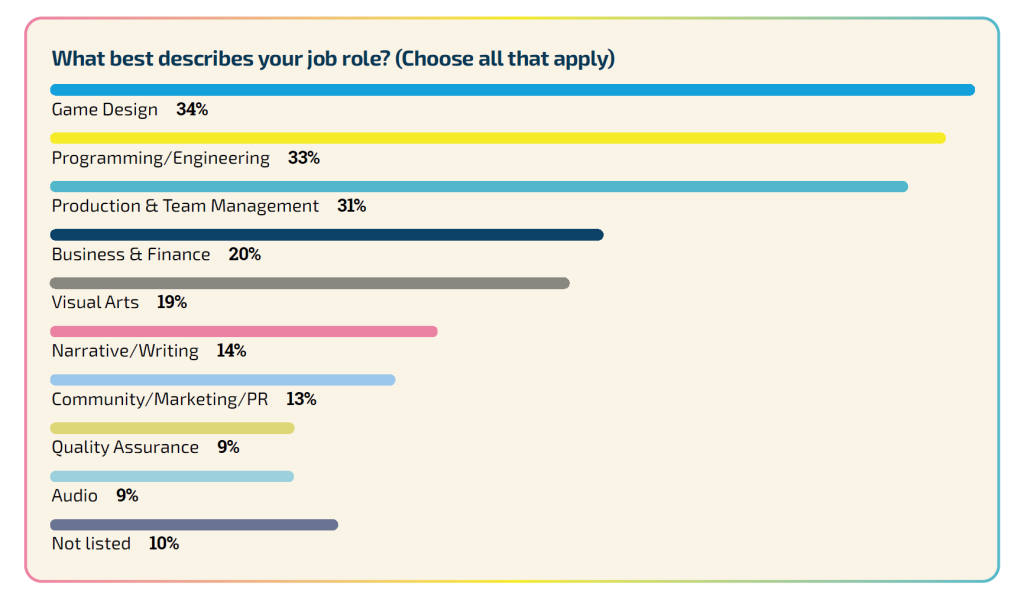
The survey indicated that the predominant job roles among respondents were in game design and programming/engineering, particularly among the younger developers. A notable 45% of those aged 18–24 years reported working in game design, while 43% were involved in programming.
Furthermore, 10% of the respondents identified with job roles that were not included in the predefined list of the survey. These roles encompass educators and students, technical artists, C-suite executives, and game researchers. Several participants also reported specializing in specific service areas such as accessibility, localization, talent acquisition, and Generative AI.
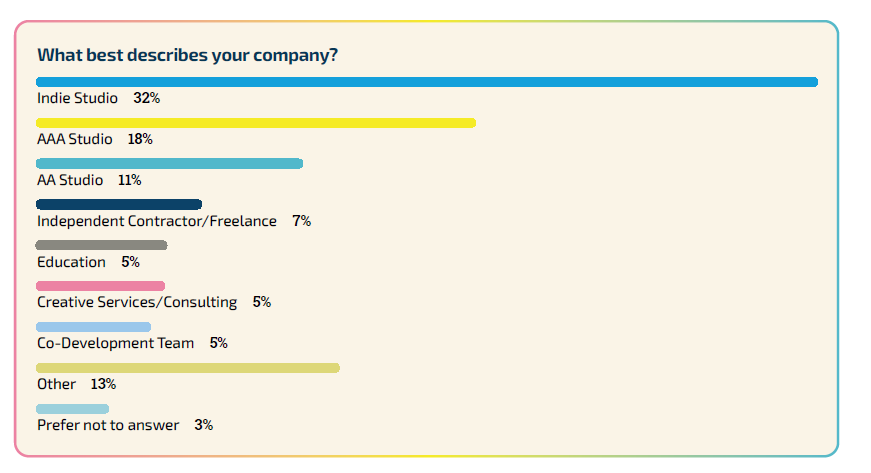
Regarding the composition of companies, 32% of survey participants indicated they are employed by independent studios, with AAA and AA studios trailing behind. A significant portion of participants (57%) are part of studios having a workforce not exceeding 50 employees. Consistent with past trends, renowned studios generally boast larger teams. Approximately three-quarters of developers in AAA studios (75%) are part of establishments with a staff exceeding 250 members, whereas an equivalent proportion of indie developers are found in studios comprising 20 or fewer individuals.
PC Continues as the Leading Platform While Developers Show Interest in the Upcoming Nintendo Switch Successor
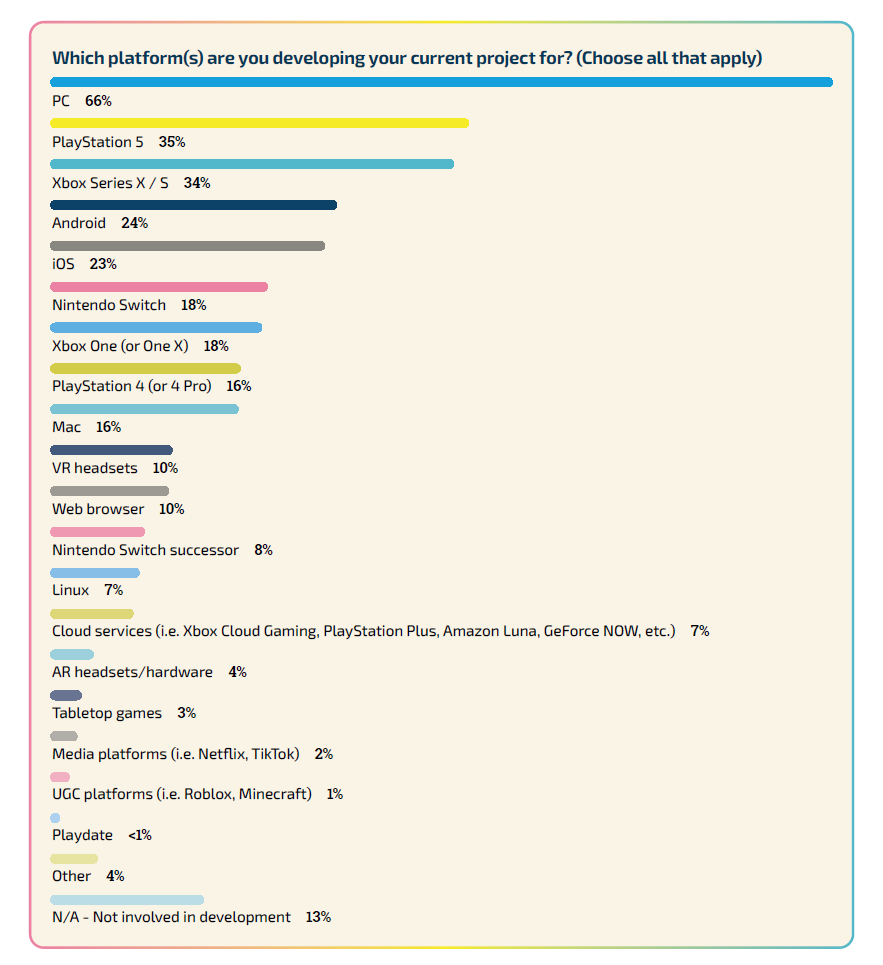
PC continues to be the platform of choice among developers, with the PlayStation 5 being the most popular console. Additionally, more developers expressed interest in developing games for the anticipated successor of the Nintendo Switch than for the Xbox Series X | S. This adds to the current trend where the PlayStation 5 outpaces the Xbox Series X | S, with 33% of developers aiming for PlayStation 5 releases versus 30% for the Xbox Series X | S. Furthermore, about 7% are focusing on cloud-based gaming services like Xbox Cloud Gaming and PlayStation Plus. The 2023 State of the Game Industry report also points to a decline in mobile gaming, with only one-fifth of developers considering Android or iOS for their next games, a 16% drop from the previous year.
A Third of Game Developers Have Either Changed Game Engines or Considered It in the Last Year
In September 2023, Unity introduced a new policy, initially covered by Game Developer, to implement a “Runtime Fee” based on the total installs of games. This decision faced significant criticism, prompting amendments to the runtime policy. In light of these events, we explored the game engines currently used by developers and whether they were contemplating a switch to alternate options.
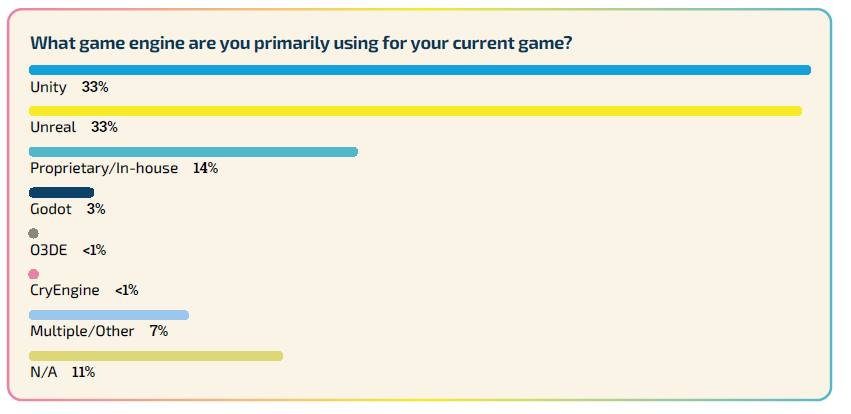
The survey indicates that Unreal Engine and Unity are the top choices among game developers, with each being the primary engine for 33% of them. These are followed by proprietary or in-house engines and the open-source Godot engine.
Yet, there’s a growing trend of developers considering a change in their game engine usage. A third of those surveyed mentioned they have either thought about switching game engines in the past year or have already made the switch, while nearly half reported no plans to switch. Many developers considering a switch pointed to Unity’s policies as a key factor. An analysis by our partners at Omdia revealed that 51% of those interested in changing engines are eyeing Godot, either as a replacement for Unity or Unreal Engine.
Emergence of Generative AI Tools in the Game Development Industry
Over the past year, Generative AI technology, including platforms like ChatGPT, GitHub Copilot, and Midjourney, has surged in popularity, becoming more accessible and widely used. We explored which Generative AI tools developers are leveraging and their concerns about these technologies.
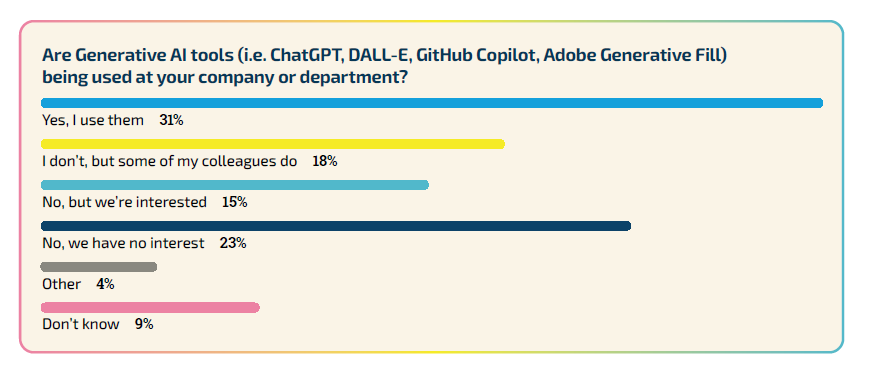
Nearly half (49%) of the developers we surveyed are using Generative AI tools in their workplace, with 31% personally using them and 18% noting their colleagues’ usage. However, about a quarter expressed no interest in these tools.
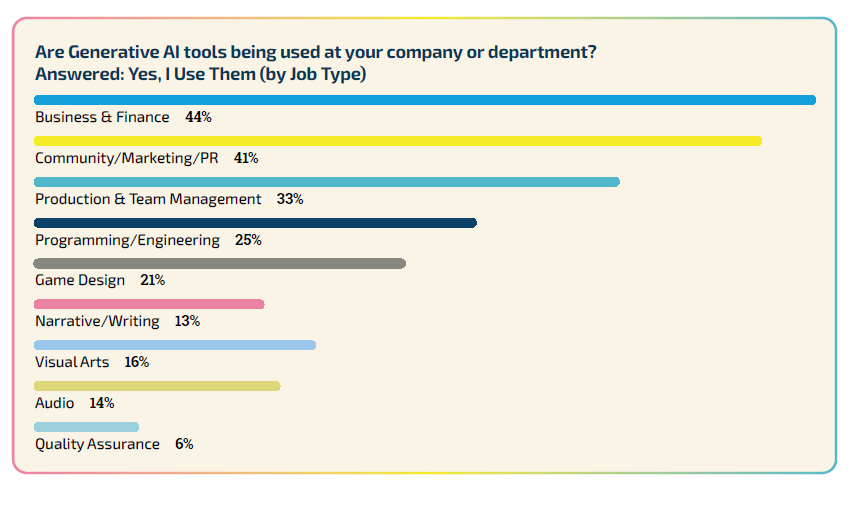
Indie studio developers are more inclined towards using Generative AI, with 37% personally utilizing it compared to 21% in AAA and AA studios. Business and marketing professionals are the highest users, whereas those in quality assurance and narrative roles are least likely to use them. Developers primarily seek Generative AI assistance in coding and accelerating content creation, alongside automating repetitive tasks. Despite the interest, some developers see no practical application for AI technology in their field.
In terms of future applications, responses varied. Some envision AI enhancing code development and optimizing creative processes, while others hope for AI tools that support rather than replace human creativity. However, there are concerns about AI overshadowing genuine creativity and not crediting original work.
Over half (51%) of developers reported that their companies have policies around the use of Generative AI, with its usage often being optional. Only 2% said its use is mandatory, whereas 12% are prohibited from using any Generative AI tools.
AAA studios are more likely than indie studios to have policies regarding Generative AI, often restricting their use. 21% of AAA developers stated their companies have banned these tools, compared to 9% in indie studios.
Eighty percent of developers express concerns about AI’s ethical implications
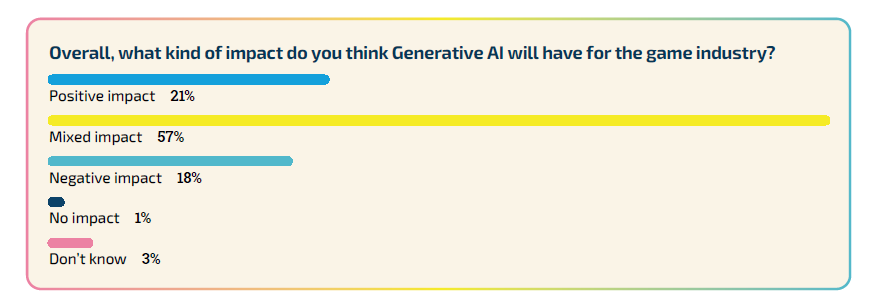
The overall sentiment among developers regarding Generative AI’s impact on the gaming industry is one of uncertainty. Most believe the impact will be mixed, while approximately 20% view it as either wholly positive or negative.
Developers in business, marketing, and programming are more optimistic about the technology’s positive influence. In contrast, those in narrative, visual arts, and quality assurance are more inclined to perceive the impact as negative.
Despite their uncertainty about the industry-wide effects of Generative AI, developers are decidedly concerned about the ethical ramifications. A significant 84% are somewhat or very concerned about the ethics of using Generative AI, with only 12% having no such worries.
Developers raised various ethical concerns about Generative AI. Some fear it could lead to increased layoffs in the gaming industry. Others are apprehensive about its potential to intensify intellectual property rights violations and the use of data without creators’ consent in training AI models.
In their own words, developers highlighted several concerns:
- The rapid development of AI technology may be overlooking potential ethical pitfalls.
- There’s a fear that management might replace or undervalue artists’ contributions.
- Adapting to change is challenging, and some may resist it.
- The industry struggles with crediting human creators, and AI could exacerbate this issue.
- AI tools are often trained using works from creators who haven’t consented to their use.
- The potential for AI to replace jobs entirely, rather than enhancing human capabilities.
- Concerns that large AAA companies might over-rely on AI, overlooking the need for human interaction.
- Ethical and copyright issues are often overlooked due to the technology’s novelty, underscoring the need for regulatory measures.
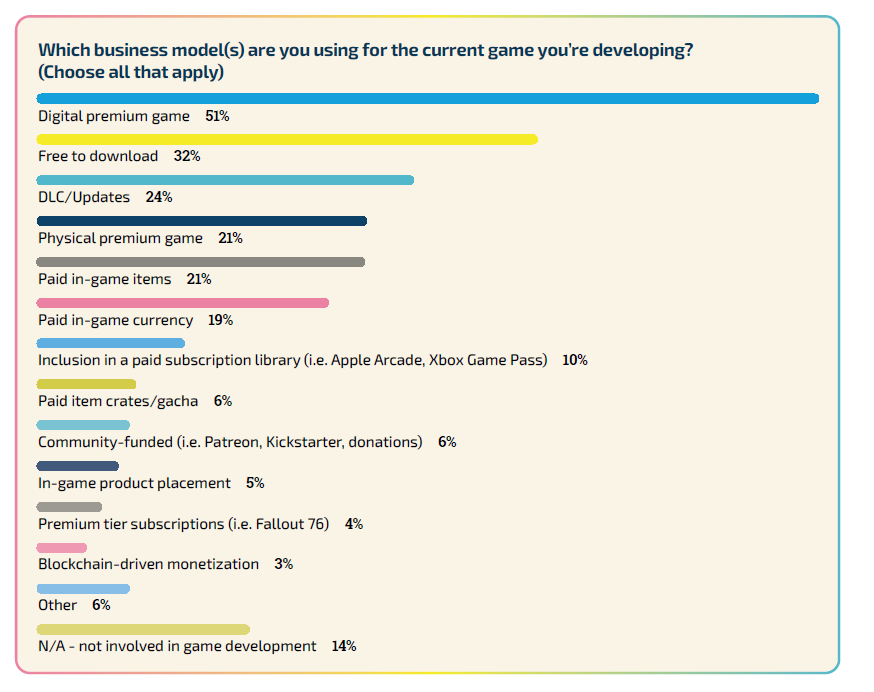
Preference for Paid Digital Download Business Model
Social Media Reigns as Top Marketing Attraction, Yet Developers Express Frustration with Twitter/X
Word of mouth and social media emerged as the primary marketing channels for game developers, with 86% utilizing each of these strategies. Close behind are real-time communication tools like Discord or Slack (74%), streaming platforms such as Twitch or YouTube (71%), and live events (71%). The less common methods include in-game crossovers and promotions (29%), influencer partnerships (57%), and paid advertising (58%).
Social media stands out as the leading marketing tool, with half of the respondents (50%) frequently using it, slightly more than word of mouth (46%). However, navigating the dynamic social media landscape presents its own set of challenges. Developers shared insights on their preferred platforms for game promotion.
Twitter/X is the most popular, used by 76% for promotion, followed by YouTube/Shorts (64%), Facebook (63%), and LinkedIn (61%). Emerging platforms like Threads, BlueSky, Mastodon, and Cohost have lesser traction, with around 10% of developers experimenting with them.
Communications, marketing, and PR professionals are more inclined to use TikTok (57% more) and Instagram (39% more) compared to other developers. In African countries, WhatsApp usage is notably higher (54%) compared to the global average (10%). Developers in Asian countries tend to favor regional services like WeChat or Line (23% each), Sina Weibo (19%), and Tencent QQ (18%), much more than their global counterparts (1-2%).
Despite Twitter/X’s widespread use, developers’ satisfaction with the platform is low. An analysis by Omdia revealed that 97% of those who discussed Twitter/X had negative feedback, citing frustrations with the platform and its owner Elon Musk, the overwhelming number of apps and platforms to manage, and a general lack of expertise or interest in social media marketing. Some highlighted the growing need for hiring specialized social media professionals.
A Quarter of AAA Developers Are Seeing Their Games Turned into Movies or TV Series
In the last year, the landscape of game adaptations into movies and TV shows has soared to new heights. Notable adaptations like The Super Mario Bros. Movie, Five Nights at Freddy’s, The Last of Us, and Dungeons & Dragons: Honor Among Thieves have achieved critical and commercial success. This trend is increasingly influencing the gaming industry.
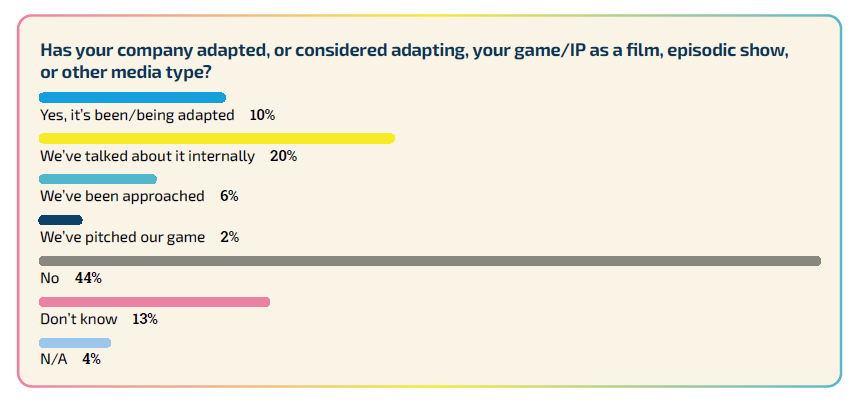
Our survey reveals that 10% of developers report their games are being, or have been, converted into films, episodic series, or other media formats. This figure rises to 26% among AAA studio developers. Additionally, 20% of all developers mentioned that their companies have internally discussed adaptations, 6% have received external approaches, and 2% have actively pitched their games for adaptation. In total, 38% of developers acknowledged that adapting their games into film and TV has been a consideration.
But do developers view this trend positively? A majority (63%) believe it’s beneficial, while only 4% view it negatively for the gaming industry. Another 26% remain uncertain. Comments from respondents highlighted a mix of opinions. Some anticipate that these adaptations could bring more visibility to their games. Others, however, are skeptical about the transferability of mediums and doubt that independent studios will benefit as much as larger ones.
Most Developers Report a Workweek of 40 Hours or Fewer
The survey inquired about the average weekly working hours of developers. Approximately two-thirds (64%) said they work 40 hours or less, aligning with past trends, and 33% specified a workweek of 36-40 hours, an increase from 29% in 2023.
Regarding the maximum hours worked in a week, 53% of the developers reported working between 41 and 60 hours. The proportion of developers who have worked a maximum of 40 hours or fewer in a week is comparable to those who have worked over 60 hours.
For those working more than 40 hours per week, 71% attributed it to self-imposed pressure. Other reasons included staff cutbacks and fear of repercussions, both new factors identified in the 2024 survey, in addition to pressure from management. Interestingly, one-third of these developers didn’t view their working hours as excessive.