Introduction to the Merchant of Record Model
A Merchant of Record (MoR) is a legal entity that serves as the official seller of record in a transaction between a business and its customers. The MoR takes on the responsibility for processing payments, managing tax compliance, ensuring regulatory adherence, and handling financial liabilities associated with online sales. This model is particularly valuable for SaaS developers and indie software publishers who want to focus on product development rather than complex tax compliance issues.
How the Merchant of Record Model Works
Legal Structure and Transaction Flow
When a SaaS company or indie developer uses a Merchant of Record service, two distinct transactions occur:
- First Transaction: The end customer purchases from the MoR (not directly from the SaaS developer)
- Second Transaction: The MoR pays the SaaS developer (minus fees and taxes)
This structure creates a legal separation that shifts tax and compliance responsibilities from the developer to the MoR provider. The following flowchart illustrates this process:
┌─────────────────┐ Purchase ┌─────────────────┐
│ │ ───────────► │ │
│ End Customer │ │ Merchant of │
│ │ ◄─────────── │ Record │
└─────────────────┘ Receipt/ └─────────────────┘
Invoice │
│ Remittance
│ (minus fees & taxes)
▼
┌─────────────────┐
│ │
│ SaaS Developer │
│ │
└─────────────────┘
Legal Responsibilities Assumed by the MoR
The Merchant of Record assumes several critical legal and financial responsibilities:
- Tax Calculation and Collection: Determining the correct tax rates based on customer location and product type
- Tax Filing and Remittance: Submitting tax returns and payments to relevant authorities
- Payment Processing: Managing the entire payment infrastructure
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to financial regulations across jurisdictions
- Fraud Prevention: Implementing and maintaining fraud detection measures
- Chargeback and Refund Management: Handling disputes and returns
- Currency Conversion: Managing international payments and exchange rates
- PCI DSS Compliance: Maintaining payment card industry security standards
Legal Shift of Tax Responsibilities
From Developer to MoR
The most significant benefit of the MoR model is the legal transfer of tax obligations. Without an MoR, SaaS developers would need to:
- Register for tax collection in multiple jurisdictions
- Calculate correct tax rates for each customer location
- File tax returns in each jurisdiction
- Maintain compliance with changing regulations
- Handle tax audits and inquiries
With an MoR, these responsibilities are legally transferred to the MoR provider, who becomes the entity responsible for tax compliance. This transfer is not merely administrative but represents a true legal shift of liability.
Legal Basis for the Shift
The legal basis for this shift stems from the reseller relationship established between the MoR and the developer:
- The MoR purchases the right to resell the software from the developer
- The MoR then sells the software to the end customer
- As the legal seller, the MoR bears the tax collection and remittance obligations
- The developer receives wholesale payments that typically don’t trigger the same tax obligations
This arrangement is recognized by tax authorities worldwide, provided the contractual relationship is properly structured and documented.
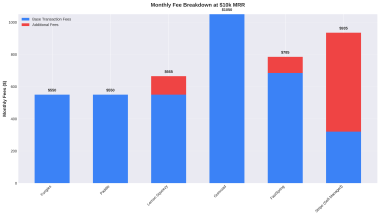
Comparative Analysis of Major MoR Providers
Feature Comparison Table
| Feature | Paddle | Gumroad | LemonSqueezy | Fungies.io |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base Fee | 5-10% + $0.50 per transaction | 3.5% + $0.30 per transaction | 5% + $0.50 per transaction | 4% + $0.30 per transaction |
| Subscription Management | Advanced | Basic | Advanced | Advanced |
| Countries Supported | 245+ | 200+ | 200+ | 190+ |
| Tax Jurisdictions | 200+ | 180+ | 190+ | 170+ |
| Checkout Experience | Overlay, Embedded, Hosted | Hosted | Overlay, Hosted | Overlay, Embedded, Hosted |
| Payment Methods | Credit/Debit Cards, PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Pay, Wire Transfer | Credit/Debit Cards, PayPal | Credit/Debit Cards, PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Pay | Credit/Debit Cards, PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Pay |
| Currencies Supported | 25+ | 20+ | 20+ | 15+ |
| API Flexibility | Extensive | Limited | Moderate | Extensive |
| Analytics & Reporting | Advanced | Basic | Advanced | Moderate |
| Fraud Protection | Advanced | Basic | Advanced | Advanced with AI |
| Customer Support | 24/7 | Limited | Business hours | 24/7 |
| Ideal For | Enterprise SaaS | Digital creators | Small-medium SaaS | Indie developers & AI startups |
Provider-Specific Strengths
Paddle
- Comprehensive enterprise-level solution
- Extensive API capabilities for custom integrations
- Advanced subscription management with dunning
- Strong focus on SaaS-specific features
- Global payment methods and currencies
Gumroad
- Simplest setup process
- Lower fees for higher volume
- Built-in audience and discovery features
- Good for one-time digital product sales
- Community-focused approach
LemonSqueezy
- Modern, user-friendly interface
- Strong subscription analytics
- Competitive pricing structure
- Growing ecosystem of integrations
- Excellent developer documentation
Fungies.io
- Specialized for indie developers and AI startups
- No hidden fees
- Beautiful checkout solutions
- No-code store builder
- AI-powered fraud detection
Practical Implications for SaaS Developers and Indie Publishers
With MoR vs. Without MoR: Responsibility Comparison
| Responsibility | With MoR | Without MoR (Direct Selling) |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Registration | MoR handles in all jurisdictions | Developer must register in each jurisdiction where sales exceed thresholds |
| Tax Calculation | Automatic by MoR | Developer must implement tax calculation logic or use third-party services |
| Tax Filing | Handled by MoR | Developer must file in each jurisdiction or hire accountants |
| Payment Processing | Integrated by MoR | Developer must integrate payment processors and handle security |
| Compliance Updates | MoR stays current | Developer must monitor regulatory changes globally |
| Fraud Management | MoR’s responsibility | Developer must implement fraud detection systems |
| Chargebacks | Handled by MoR | Developer must respond to and manage disputes |
| Customer Payment Issues | First-line support by MoR | Developer handles all payment support |
| International Expansion | Immediate with existing MoR | Requires research and setup for each new market |
| Legal Liability | MoR assumes primary liability | Developer bears full liability |
Resource Requirements Comparison
Human Resources Needed
| Role | With MoR | Without MoR |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Specialists | Not required | 1-3 FTEs or external consultants |
| Compliance Officers | Not required | 1 FTE or external consultant |
| Payment Operations | Minimal | 1-2 FTEs |
| Financial Analysts | Minimal | 1 FTE |
| International Tax Consultants | Not required | External consultants per region |
Time Investment (Monthly)
| Activity | With MoR | Without MoR |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Compliance | 0-2 hours | 20-40 hours |
| Payment Reconciliation | 1-2 hours | 10-20 hours |
| Regulatory Updates | 0 hours | 5-10 hours |
| Customer Payment Support | 1-5 hours | 10-30 hours |
| Financial Reporting | 1-3 hours | 10-20 hours |
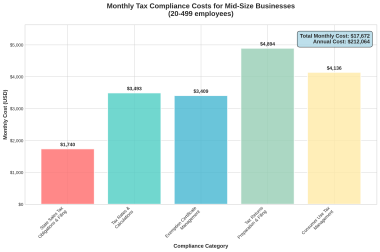
Cost Implications
Direct Costs
| Cost Category | With MoR | Without MoR |
|---|---|---|
| Service Fees | 3.5-10% of revenue | 1-3% payment processing fees |
| Tax Registration | Included | $500-$5,000 per jurisdiction |
| Tax Filing | Included | $200-$1,000 per filing per jurisdiction |
| Compliance Software | Included | $200-$1,000 monthly |
| Payment Infrastructure | Included | $100-$500 monthly + setup costs |
Indirect Costs
| Cost Category | With MoR | Without MoR |
|---|---|---|
| Compliance Risk | Minimal | High (potential for fines) |
| Opportunity Cost | Low (focus on product) | High (resources diverted from core business) |
| Scaling Friction | Low | High (each new market adds complexity) |
| Time to Market | Fast | Delayed by compliance setup |
Real-World Implementation for Different Business Sizes
Solo Developers and Micro-SaaS
For individual developers or very small teams (1-3 people), the MoR model offers significant advantages:
- Immediate Global Reach: Sell worldwide from day one without tax registration concerns
- Focus on Product: Dedicate limited resources to product development rather than compliance
- Predictable Costs: Service fees are proportional to revenue, avoiding large upfront compliance investments
- Reduced Complexity: Simplified financial operations with consolidated reporting
Recommended MoR Providers: LemonSqueezy or Fungies.io for their indie-friendly pricing and simplicity
Small SaaS Teams (4-20 employees)
Small teams benefit from the MoR model through:
- Scalable Operations: Grow without proportionally increasing compliance workload
- Market Expansion: Enter new markets without additional compliance research
- Resource Allocation: Keep the team focused on product and customer acquisition
- Risk Mitigation: Reduce exposure to compliance errors during growth phases
Recommended MoR Providers: Paddle or LemonSqueezy for their balance of features and pricing
Medium to Large SaaS Companies
Even larger companies can benefit from the MoR model:
- Compliance Outsourcing: Delegate specialized tax knowledge to experts
- Operational Efficiency: Streamline financial operations across multiple products
- Risk Management: Transfer compliance liability to a specialized partner
- Focus on Core Competencies: Maintain organizational focus on product innovation
Recommended MoR Providers: Paddle for its enterprise features and global reach
Case Studies: MoR Impact on SaaS Businesses
Case Study 1: TypingMind (AI Startup)
Challenge: Managing sales tax was a “constant headache” and “complicated and intimidating task” for this AI startup.
Solution: Switched to LemonSqueezy as their MoR provider.
Results:
- Eliminated all tax compliance concerns
- Increased MRR by 1300%
- Generated $200,000 in revenue within 4 months of switching
- Founder could focus entirely on product development and marketing
Case Study 2: Anonymous SaaS Company (50 employees)
Challenge: Expanding internationally triggered tax registration requirements in multiple countries.
Solution: Adopted Paddle as their MoR.
Results:
- Avoided establishing legal entities in 12 countries
- Saved approximately $500,000 in compliance costs
- Accelerated international expansion timeline by 18 months
- Reduced finance team requirements by 3 FTEs
Case Study 3: Solo Developer with Educational Software
Challenge: Received notice of tax non-compliance from three US states and faced potential penalties.
Solution: Migrated to Fungies.io as MoR.
Results:
- Resolved compliance issues immediately
- Expanded sales to 30+ countries without additional compliance work
- Maintained lean operation with zero compliance staff
- Focused 100% of development time on product improvements
Limitations and Considerations of the MoR Model
Potential Drawbacks
- Cost: The percentage-based fees can become significant at higher revenue levels
- Brand Control: The MoR appears as the merchant on customer credit card statements
- Integration Complexity: Some customization limitations compared to direct selling
- Dependency: Business operations rely on the MoR’s systems and stability
- Data Access: Some customer payment data remains with the MoR
When MoR May Not Be Ideal
- Very High Volume/Low Margin: When transaction fees significantly impact profitability
- Highly Customized Checkout: When unique payment flows cannot be accommodated
- Specific Payment Methods: When required payment options aren’t supported by MoRs
- Regulatory Requirements: When specific industries require direct merchant relationships
Sources
- Paddle – “What is a merchant of record (MoR) + why use one for payments and sales tax?” (August 1, 2024)
- SubscriptionFlow – “Understanding the Importance of a Merchant of Record for Digital Products” (April 1, 2024)
- Fungies.io – “The Vital Role of Sales Tax Compliance in SaaS Business Success” (September 17, 2024)
- LemonSqueezy – “Everything you need to know about a Merchant of Record vs a Seller of Record” (January 26, 2024)
- Cleverbridge – “What is a Merchant of Record (MoR)?” (March 12, 2024)
- FastSpring – “What Is a Merchant of Record? (And Why Should You Care?)” (September 24, 2024)
- PayPro Global – “Merchant of Record Compliance: Regulations, Tax, and Fees” (December 11, 2023)
- The Payments Association – “Understanding the merchant of record model: A key to simplified global payments” (November 11, 2024)
- CheckoutPage – “What is a Merchant of Record (MoR)? (And do I really need one?)” (January 24, 2025)
- Easy.tools – “Merchant of Record – Is it always the best choice?” (January 30, 2025)